The Workplace Management Framework (WMF) provides a structure for the development and subsequently the assessment of best practice in the management of the workplace.
‘Workplace Management is the management of all resources needed to design & maintain appropriate, effective and economical workplace experiences that align to strategic business objectives and support people in doing their best work every day, wherever they are.’
The role of ‘Workplace Management’ emerges as an integrator of contributions from across a number of disciplines (Corporate Real Estate, Facilities Management, IT, Human Resources, Risk, Security etc.) to deliver an economic and effective ‘workplace experience’ to an organization’s people. (Get your FREE copy of the Framework HERE )
)
The purpose of the Framework is to:
- – Define the management disciplines needed
- – Maximize the strategic and economic benefit of the workplace
- – Enable the development of best practice organizational and people capabilities
- – Align the day to day delivery of workplace experiences to the core purpose of the organization
- – Communicate the management requirements needed
- – Measure and to demonstrate the effectiveness of the organization
- – Enhance the professional standing of the Real Estate and Facilities Management
- – Communicate clearly the nature, purpose and structures associated with management of the workplace
The WMF is designed to be applied to all types of workplaces and embraces:
- – ‘High-Tech’ workplaces, (including Power Stations, Data Centers and Industrial Premises), through to
- – ‘High-Touch’ workplaces, (these include Offices, Serviced Offices, Homes and people working On the move).
- – In between these two extremes we have workplaces such as Hospitals, Schools, Universities and Prisons.

The scope of Workplace Management embraces the ‘workplace experience’ that would be appropriate in all the places people work (inside and outside office buildings) and embraces not only the practical issues associated with effective work, but also the emotional and sensory aspects.
Organizations are ultimately the aggregate energy of large numbers of people harnessed together within structures and processes to deliver a defined outcome.
Components of the Framework
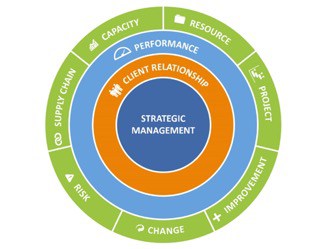
The Framework consists of 10 management capabilities and provides a vehicle for determining how well the organization achieves best practice in the management of its workplace.
 STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
Strategic Management is concerned with:
- – the innovative alignment of workplace assets and services with the core purpose of the organization, and
- – the creation of the mechanisms by which the workplace and services are effectively and economically designed and delivered on a day to day basis.
To be successful, leaders responsible for the workplace need to actively work to be credible, confident business contributors, knowledgeable about the organization at large, the wider strategy for the business, with the most up to date trends in people management, technology, engineering, service management and innovation.
Innovation is primarily about releasing every person within the functions responsible for workplace to think creatively and come forward with new ways of delivering more value to the enterprise in relation to its businesses strategy and needs.
The availability of mobile technologies has enabled a major shift in working patterns. People can choose to work in ways that best match their jobs and personal circumstances. Particularly in ‘high touch’ work environments, careful consideration needs to be given to the design of the ‘workplace experience’ constructed from all the interlocking services that are provided.
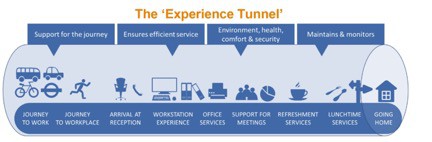
‘To design an experience you need to think through, second by second, the fusion of sounds, sights, information, web pages, smells, spaces, images, interactions, human behaviours and processes to create an experience that is both effective, energising and which subtly reinforces brand values.’
The idea of an ‘Experience Tunnel’ represents the individual’s perceptions of his environment minute by minute through a working day in relation to all of their senses.

CLIENT RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT
This capability is concerned with:
- – the development and maintenance of effective relationships with internal clients and consumers to gain an intimate knowledge of future plans, demand for the workplace, and
- – the proactive evolution of the workplace experience to deliver greater value at an economic cost.
The main objective of Client Relationship Management is to act as a communication bridge between two parties,
- 1. the ‘clients’, the senior leaders whose businesses pay for services and space, and
- 2. the ‘consumers’, who are the people who use the services, environments and experiences each day
The interpretation of business needs and development of immediate and short term demands, concerned with meeting existing requirements and supporting changes for workplaces and services represent an important role for the Client Relationship Manager.
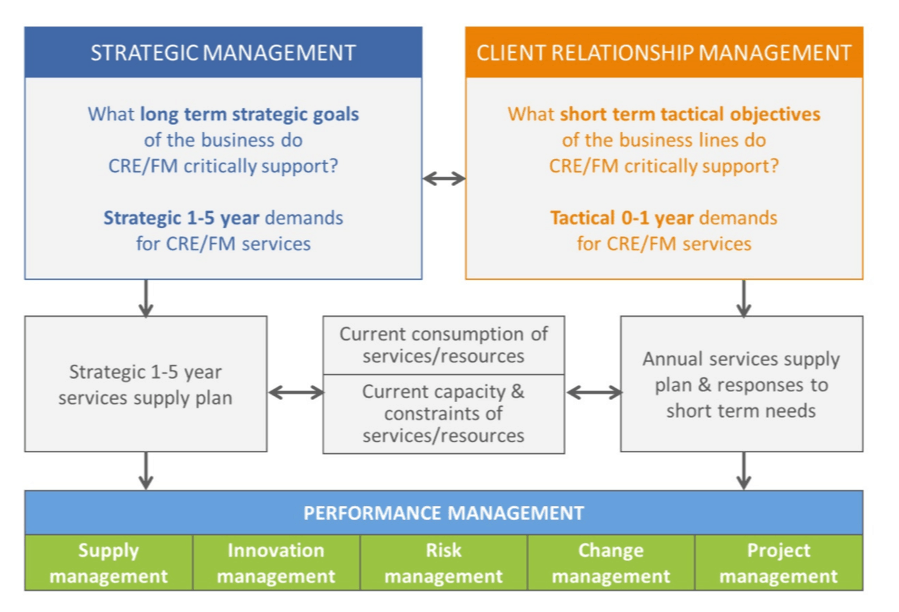
 PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT
This capability is concerned with:
- – defining and measuring the performance needed from all parts of the Framework to enable the delivery of effective workplaces at an economical cost, and
- – setting up processes and mechanisms to ensure improvements in service.
The most important part of Performance Management is in the use of data to enable the engagement of all parties (the business, suppliers, staff, occupants and customers) in innovating to achieve desired outcomes.
It is a key responsibility of workplace leaders to improve the quality of the services for which they are responsible and to encourage openness in acknowledging problems and failures, analyzing root causes and working to eliminate those causes.

SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
This capability covers the entire supply chain life cycle from:
- – strategic policies and plans,
- – selection of suppliers of all the workplace assets and services,
- – the negotiation of contracts and where appropriate the termination of contract,
- – the governance of supply chain relationships, and
- – the performance management of supplied services.
The aim is to create arrangements which align supplier activities within the supply chain to the organization’s objectives and ‘workplace experiences’, recognizing the volatility of the organization’s business situation and the probability of the need for change in volume or nature of services.
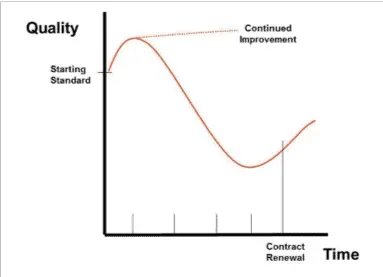
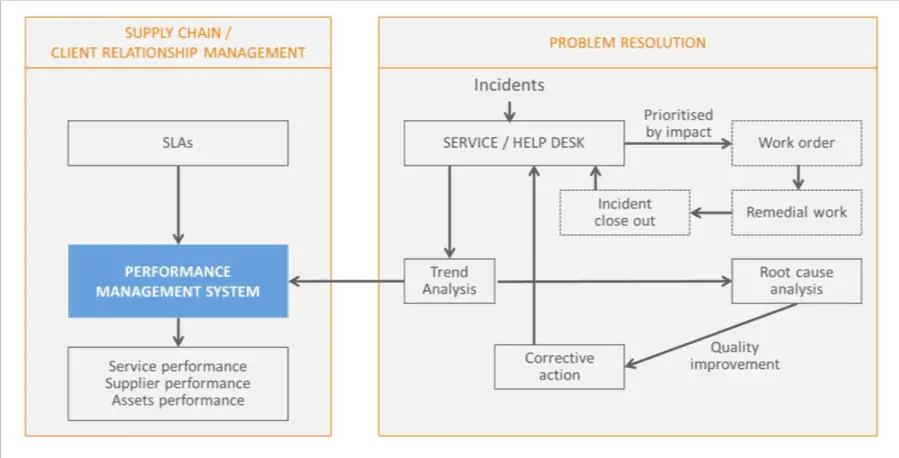
The rapidly changing business environment requires that suppliers are positively responsive to change and best practices should encourage agility to change and innovation in supply, by eliminating the adverse trends that often characterize adversarial supply relationships as illustrated in the figure below.
![]()
CAPACITY MANAGEMENT
This capability is concerned with:
- – the provision of appropriate levels of capacity and commitments to the physical workplace, services and technologies needed to achieve the organization’s strategic purpose in the most economical manner.
Capacity Management is primarily about:
- – To maintain a precise understanding of the true capacity of the workplace, services and technologies to support the business.
- – To continually measure the level of consumption of the capacity.
- – To use knowledge of consumption of capacity to improve the effectiveness and resilience of services and the workplace.
- – To maintain an appropriate balance of the workplace ‘supply’ in relations to short and long terms business needs and the levels of volatility of the business.
- – To enable effective decisions about commitments to future workplace capacity.
![]()
RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
This capability is concerned with:
- – day to day management of resources needed to deliver effective workplaces.
Resource Management covers physical assets but also the human resources and utilities that are consumed and its aim is to:
- – Ensure that that the organization has the right number of suitably trained and motivated people
- – Ensure that the best in class management techniques are deployed
- – Form decisions based on evidence of actual consumption of services, space, systems, services and other resources
- – Enable short term changes in demand to be balanced against available capacity
- – Enable the efficient use of the workplace to deliver on sustainability requirements
![]()
IMPROVEMENT MANAGEMENT
This capability is concerned with:
- – improving the provision of services and environments through a culture of innovation.
Most leaders with responsibility for managing the workplace would regard the resolution of day to day problems and failures as the most fundamental of all their operational responsibilities with outcomes:
- Workplace services and experiences that meet the requirements of all clients and users.
- Failures being dealt with swiftly and economically.
- Lessons being learned leading to the elimination of repetitions through a continuous improvement process.
![]()
RISK MANAGEMENT
This capability is concerned with:
- – the management of all forms of risk that impact upon the ability of people and the workplace to work effectively,
- – the identification and analysis of sources of risk and those practices that minimize its impacts, and
- – how recovery from failures and disasters will be handled.
The scope of risk management includes:
- – Security of physical and information assets
- – Health & Safety risks to people
- – Risks arising from change and projects
- – Risks to the effectiveness of work arising from failure of delivery of services
- – Environmental risk
- – Business Continuity Planning
All the above are essential to reduce the likelihood of security incidents, failures in projects, services and workplaces and reducing any adverse impact upon the business.
![]()
CHANGE MANAGEMENT
This capability is concerned with:
- – best practices in promoting, managing, and supporting changes in the way in which the workplaces are used and managed.
- – the formulation of strategies and processes needed to make effective changes to locations, space, technologies, systems, processes, behaviors or services to improve the effectiveness of the business,
- – technically, behaviorally and politically complex change programs, and
- – arrangements that will ensure the changes implemented are maintained and evolve.
Mobile technologies are enabling new ways for people to make their contribution to their organizations. To take advantage of these new opportunities requires a careful and conscious programme of activities to prepare:
1. The workplace (IT, telecoms, and space),
2. The organization (security, risk, leadership, processes) and
3. The people (behaviors and working practices) for the transition to new forms of working.
The modern workplace is a complex system which need well-developed relationships and understandings between all the parties that have to work together to deliver the change e.g. consumers, IT, telecoms, building services, space planning, project management etc.
![]()
-
PROJECT MANAGEMENT
This capability covers:
- – best practices and development of skills and processes that deal with the management of projects from ‘inception’ to ‘business as usual’. This includes justification, governance, financial management and change management, to implementation, completion and post project review.
To achieve specific project deliverables on time and on budget this capability requires skills in:
- – planning,
- – organizing,
- – motivating,
- – controlling resources, procedures and protocols
Workplace projects range from small moves and changes involving little risk to the business to large relocations, new builds across multiple geographic domains. Effective project management involves a rigorous planning process to:
1. Meet project sponsors requirements.
2. Achieve desired outcomes.
3. Learn from past experiences.
(Get your FREE copy of the Framework HERE )
)
