With the technologies going smarter, so do the hacking methods and it’s easier than ever to fall a victim to these attacks. If you have any device connected to the internet, there is a risk of getting hacked. And the stats are speaking for itself: according to the study conducted by Michel Cukier, hacking attacks occur every minute. Unfortunately, due to the lack of security, many of these attacks appear to be successful. One more alarming fact is that from the beginning of 2020 the number of exposed data records reached more than 8 billion (as per the report by Risk Based Security).
While these cyber threats can bring inconveniences to individuals, their impact on businesses is devastating, as it puts at risk not only the reputation and client’s trust but can wipe a company off the market. That’s why raising security awareness is critical both for business owners and their employees to be ready to counteract malicious attacks. Various cyber-security courses , professional literature, and training can contribute to this goal. Acquaintance with the ways used for system exposure and understanding their risks is the first step in improving the security of your company, so in this article, we gathered the most popular security threats and ways to avoid them:
, professional literature, and training can contribute to this goal. Acquaintance with the ways used for system exposure and understanding their risks is the first step in improving the security of your company, so in this article, we gathered the most popular security threats and ways to avoid them:
Social Engineering
This one involves minimum technology inputs and is aimed at hacking humans. While machines are programmed to strictly follow certain rules, and with the evolution of artificial intelligence can learn how to recognize and prevent intrusions, humans are flexible and more vulnerable due to their emotions and feelings like fear, desire to help and compassion. By triggering these feelings and pretending to be the CEO, clients, company partners, representatives and even relatives of your colleagues social engineers can obtain almost any kind of information they need.
Since social engineers are great manipulators and psychologists, it might be hard to resist their psychological pressure and influence. That’s why it’s vital to introduce strict security policies for your employees including but not limited to automatic ways of client verification ((i.e. analyzing the IP addresses used for logins, phone numbers, previous contacts etc.) so that humans are eliminated from this process). Identify what internal information can be shared with your clients and what needs to be kept in secret (i.e. the software you use for client’s correspondence, and system protection, how many workers are employed in the company, what shifts they are working, and what are the internal protocols). Some of this information may seem to be useless, but combined together it may give an attacker privileges to find the weak system points.
There are many strategies and tricks in social engineering. Here are the most common social engineering attacks: Phishing, Vishing and Email Spoofing.
• Phishing is the most widely used scam where the domain names and websites are duplicated to look almost the same as a real source to deceive targets into exposing their login details to most commonly used services or give out credit card information.
• Vishing is a voice version of phishing also known as phone scam where villains overwrite the real phone numbers with some public ones combining real conversations with voice messages, and pretend to be bank representatives or people you know to get the internal information that should not be shared with third-party.
• Email Spoofing is similar to the vishing but in this case, the forgery of email headers occurs to overwrite the information about the sender and as a result spoofing emails seem as if it’s coming from the real person or organization. Usually, these emails are sent from the open relay servers (that do not require to log in to the email account to send emails from it) and are delivered to the spam folder.
Three of these methods are related to forgery of existing trusted resources and sometimes are used together to increase the effectiveness of an attack. For instance, you receive an email from your bank with malicious links inside and then “a bank representative” contacts you to confirm it and open the link to create a vision of a legitimate situation.
Here’s the example of spoofing (imitating PayPal as a sender) combined with phishing (leading to the website that is not an official PayPal one to make users expose their login details to use them later for unauthorized financial operations on clients’ behalf.

Source: http://www.consumerfraudreporting.org/phishing01paypal.php
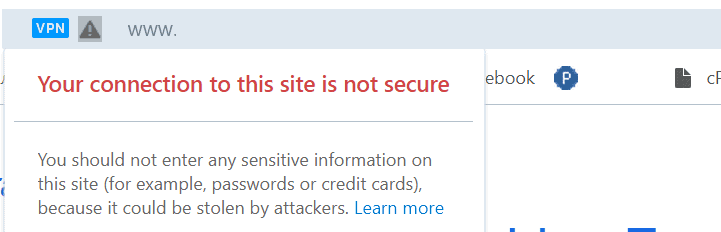
How to avoid: If you are contacted by someone by email or phone pretending to be your bank representative, colleague or boss asking you the details they should know or some confidential info (like CVV), drop the phone and contact them by the official email they provided to you. It goes without saying that the links and attachments in the emails that are coming from people you do not know should be never ever opened. In case of phishing, usually these resources contain grammar mistakes and there are design flaws that should evoke suspense. Besides, they are not protected by SSL certificate (do not have a green padlock near the address and the in browser like the one below:
should be never ever opened. In case of phishing, usually these resources contain grammar mistakes and there are design flaws that should evoke suspense. Besides, they are not protected by SSL certificate (do not have a green padlock near the address and the in browser like the one below:
DDoS Attacks
DDoS, deciphered as distributed denial of service attacks are frequently used to disrupt web services through traffic overloading. In a nutshell, they simulate the requests from real users to one or several points in the network including websites, client’s portal and other systems. They can be hard to mitigate since the traffic originates from many different sources which makes it impossible to block all of them at once.
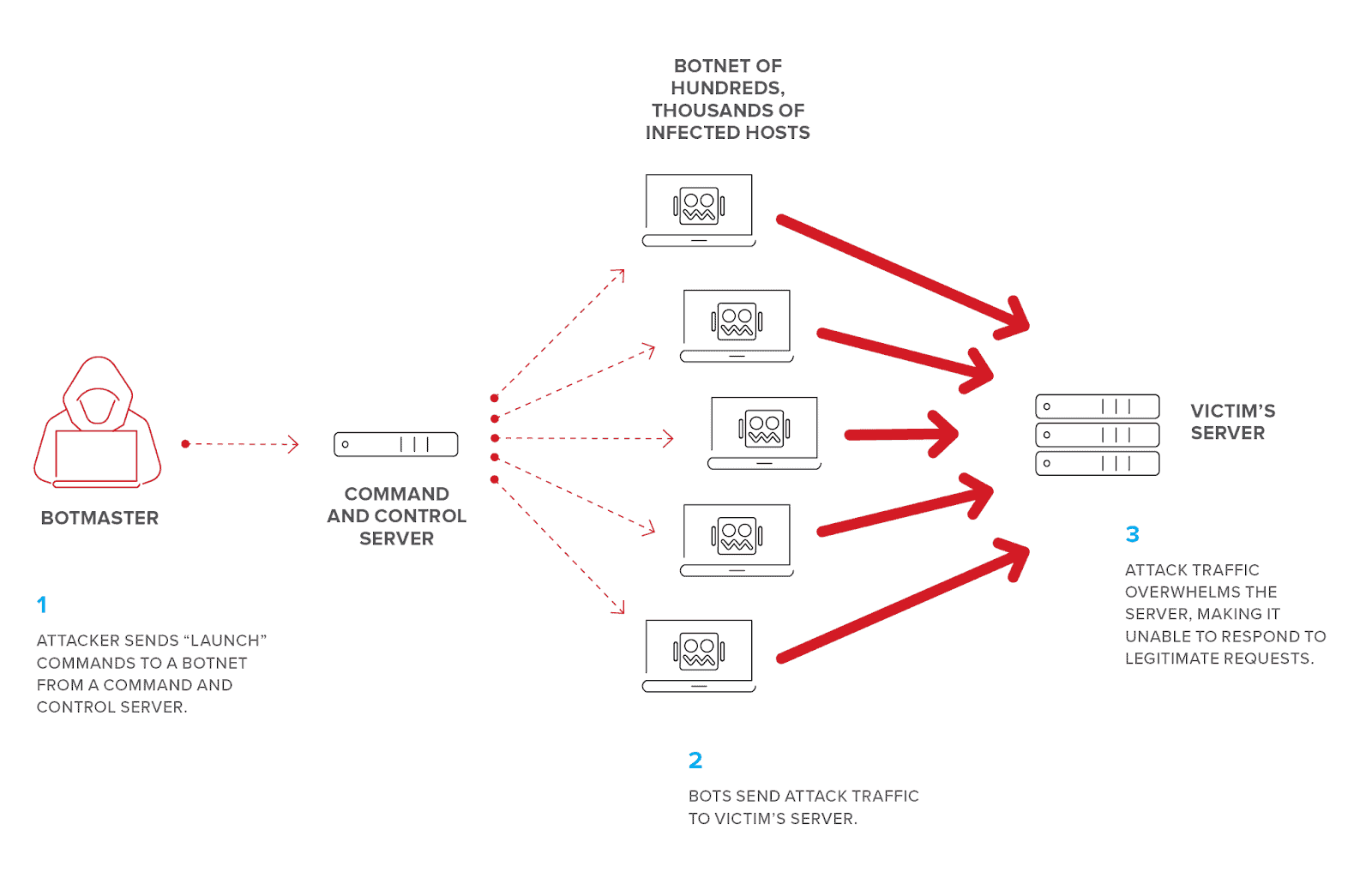
Source: F5
How to avoid: The security measures to avoid these attacks should be taken on multiple levels starting from adopting network protection solutions like Imperva, load balancing, protecting most common ports, and restricting the access to internal resources via VPN services, so that all the incoming traffic from external networks is blocked. Unfortunately, there is no 100% way to secure from these attacks, however, elaborating mitigation strategies can help to minimize the negative effects, if a DDoS attack occurs.
can help to minimize the negative effects, if a DDoS attack occurs.
Infecting System with Malware
Source: SonicWall
One of the most disastrous security threats is Malware uploaded to the target systems for different reasons. While malware is associated with Trojans, worms and viruses that modify source code of applications to destroy information and make systems inoperable, its application is wider:
• Spyware – used to gather information like login details, level of accesses, internal documents and other parts of systems in a way that a user is not aware of the attack. The obtained info may be used for blackmailing, advertisements, and destroying company reputation revealing internal data. It includes keyloggers to gather the information entered on the keyboard as well as rootkits that allow remote commands execution and connection to exposed devices.
• Ransomware – used to encrypt computer data so that they become inaccessible to retrieve or use and if the ransom is not paid, the sensitive data will be exposed or destroyed. This one is used mainly for extortion and blackmailing
• Adware – the most innocent type of malware annoying users with continuous ads, pop ups and banners on all the websites. However, sometimes it can also initiate viruses and spyware once you click on ads.
They enter a system in different ways starting from visiting untrusted websites, software backdoors like cross-scripting, MySQL injections, PHP exploits. They also come as email attachments and malicious links masked as something different
How to avoid: Make sure to install the trustworthy firewall with constantly updating signatures that filters incoming traffic, as well as anti-malware software that prevents and acts as a watcher. It will detect the infection of the existing files and put them in quarantine. If you use some chat or ticket system to communicate the make sure that the attachment types are restricted only certain formats and block extensions like .exe, .rar, .dll and make sure to have the an anti-virus software that checks commonly used files lille .docx, or .pdf as these files can contain macros inside the files to distribute malware. It’s also worth instructing your employees to avoid opening links from unknown sources and if some links are sent by clients, it’s better to check them not directly on a working desktop but using a virtual machine to minimize the risks.
Takeaways
When it comes to the education of your employees, it’s better to conduct extensive cyber security training for beginners before a person starts working to ensure that s/he is aware of the consequences of attacks and how to recognize them. One more motivational factor for further learning is conducting security workshops and sending reminders on security updates in the company that can impact their work.
training for beginners before a person starts working to ensure that s/he is aware of the consequences of attacks and how to recognize them. One more motivational factor for further learning is conducting security workshops and sending reminders on security updates in the company that can impact their work.
Knowing these risks will help you to make informed decisions related to the protection of your system from external intrusion events and treat cyber security more seriously reflecting it in the internal policies. This may include setting strong passwords and their automatic rotation if users fail to change them on their side. Ownership verification, data sharing, internal monitoring systems, protection software, regular server backups and handling security incidents — just to name a few.
Apart from that, it’s highly recommended to invest in skilled internal security specialists and conduct external security audits from time to time. It will help to ensure the safety and integrity of your system.
Last but not least is creating trust and transparency in reporting security breaches. The sooner a breach is noticed, the less consequences it will have. That’s why it’s better to encourage reporting the breaches or any suspicious situations and conduct no-blame retrospective analysis of all dangerous situations. If your employees are afraid to report a breach or mistakenly downloaded file because they can be penalized, regardless of the software you use, it will not be effective.

