The efforts for creating a bigger awareness of cleaner, sustainable environments are on the rise. There is an increased interest among corporations for building “greener” and environmentally friendly buildings. One of the most popular certification programs for green building is LEED.
What is LEED Certification? LEED Certification process is a program for designing and building energy-efficient and water-conserving buildings, for which construction will be used green and sustainable materials and resources. This program consists of a few rating systems regarding design, construction, operation, and maintenance of different types of buildings, for which the projects earn points.
Depending on the points certain project receives, the building after it’s finished will receive one of the four LEED certifications; Certified (40-49 points), Silver (50-59 points), Gold (60-79 points), and Platinum (80-100 points).
The LEED program (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) is developed in the 1990s by the non-profit USGBC (US Green Building Council) in order to encourage organizations, companies, and individuals in adopting green and sustainable designs.
This program is mainly focused on projects for new and commercial buildings but can be also used for restoring the older ones. The program is not mandatory for the companies, but certain buildings that are LEED-certified in some states might receive certain incentives, such as tax credits, local tax breaks, grants, fee waivers, etc.
In order to receive a LEED status, the companies need to make some high expenditures upfront, that after some period of time will present massive cost savings.
LEED Rating Systems
LEED standards are pretty flexible and can be applied to all building types no matter the phase of development. LEED Rating Systems are grouped into five categories according to which the project teams are organizing their processes and documentation.
- – Building Design and Construction
- – Interior Design and Construction
- – BuildingOperations and Maintenance
- – Homes
- – Neighborhood Development
Building Design and Construction – BD+C
This category has 10 rating systems within, which present as guidelines for building new buildings and renovating old buildings. New construction and Core and Shell are the main certificates from this category. Under core and shell projects are the ones where the developer controls all the electrical, mechanical, fire protection, and plumbing, without touching the interior build-out.
As an example of buildings that belong to this category are schools, data centers, hospitals, warehouses, retail, office buildings, apartment buildings, etc.
Interior Design and Construction – ID+C
This category consists of projects that are complete interior fit-out. This category was designed for project teams that don’t have control over the building or are leasing part of a bigger commercial building but want to design an interior space that will improve the environment and the people that are part of that organization.
Interior spaces that are part of commercial buildings, hospitals and retail are examples that fall in this category.
Building Operations and Maintenance – O+M
This category is intended for buildings that already exist and are inefficient. The goal is by retrofitting these buildings to improve their sustainability in the overall operating systems and maintenance. However, these buildings have a less sustainable impact on the environment, than the brand new and sustainable buildings.
This category includes any type of office space, schools, existing warehouses, data centers, hospitals, retail buildings, etc.
Homes
The LEED program for homes became available in 2008 to the public. This program was designed for family homes that are no more than three stories tall, no matter if they are multi-family or single residential buildings.
LEED is updating its score system over some period of time in order to include all the advancements in the building industry.
Neighborhood Development ND
The final category of LEED rating systems is meant for Neighborhood Development. This program is intended for all land projects, whether new or redevelopment ones. It is integrating all principles of designing walkability, smart growth, green spaces, urbanism, etc., from planning to completion of the project.
Additional categories:
Cities and Communities
This category is intended for entire cities as well as certain sub-sections of the city. LEED for Cities consists of tools for measuring and managing the water consumption of the city, its energy use, transportation, waste, human experience, etc.
LEED Recertification
This category is for all projects that have been previously certified under LEED – including Building Design and Construction (BD+C) and Interior Design and Construction (ID+C), no matter their initial version or rating system.
LEED Zero
This category is available for all projects that are already certified under Building Design and Construction (BD+C) or Building Operations and Maintenance (O+M), or are registered for receiving an O+M certification. LEED Zero is meant for all projects that have net-zero goals in resources and carbon.
LEED Certification Process
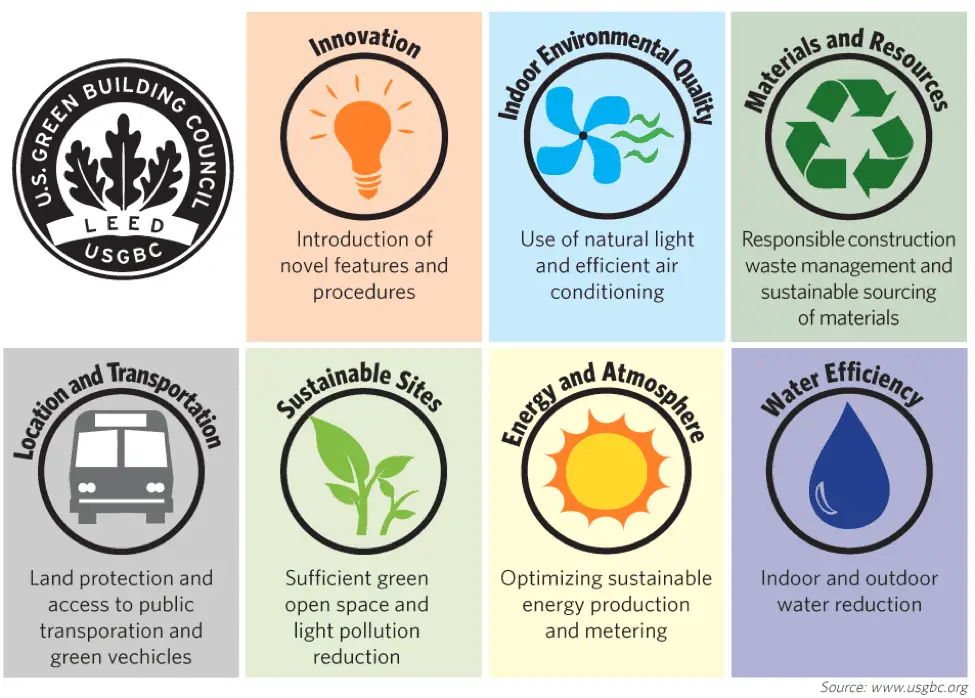
LEED certification process consists of receiving points for several categories. Each of these categories suggests several opportunities to be used and integrated into the projects. When a certain project meets the required criteria from these categories earn points. The higher the number of points, the more sustainable and energy-efficient is the building. The categories that are measured by LEED are:
Location and Transportation – This category is regarding the proximity of your project to the transportation options in the area, and how the users can access the building without a problem. Also, bonus points are rewarded if the project is built near water or sewer lines, so its building doesn’t disturb the land by installing additional infrastructure. Then where the commercial building or home is built in relation to the surrounding infrastructure, other buildings, neighborhoods.
Homes, for example, can receive extra points for not being located near endangered species, floodplains, no disturbance zones (zones where certain trees or plants should not be disturbed), etc.
Materials and Resources – This category is regarding the use of earth-friendly, sustainable materials, re-use, renewable materials, recycling, etc. Then reducing the waste and its impact on the environment.
Conserving resources and recycling is a popular topic these days. LEED’s guide is covering the overall construction process so there are specific limits on waste for every type of building material. When you are trying to receive LEED certification for your project, make sure that you or your builder understand the importance of using proper materials as well as conserving them.
Water Efficiency – This category is regarding designing the building in a way that the usage of potable water will be reduced as well as reusing greywater. Conservation of water is a major focus of LEED’s guide. This measure arose because of the increased demand for water in industrial processes and personal use.
Homes, for example, can conserve water by harvesting rainwater in barrels or different systems for watering the plants and even for drinking – after the rainwater is filtered.
Also, the project can receive additional points for installing a system for greywater recycling and making this water potable. Greywater is leftover water from sink drains, showers, and clothes washers, and it’s non-potable water.
Installing these systems can be quite expensive, but in the long run, you will save on utility bills.
Energy and Atmosphere – This category is regarding improving energy performance and promoting better indoor air quality.
Sustainable Sites – This category is regarding designing the project in a way that won’t affect the environment, but the natural resources and ecosystems around the building will take part in its design and it will minimize the pollution of the environment.
Regional Priority Credits – This category is addressing certain concerns connected with a specific location or area. The project will receive additional points for including upgrades that help in solving regional environmental concerns or problems.
For example, if the project is located in the southeastern USA, you will be faced with a big number of sunny days throughout the year and installing solar panels will get you additional points. Or getting additional points for incorporating systems that prevent erosion for the irrigation water in the rural areas.
All of the US can receive special credits according to this category, as well as international projects.
Innovation in Design – This category is for awarding points for any strategies or ideas that are inventive and sustainable and are not included in the LEED Rating System, so they can be properly awarded.
Indoor Environmental Quality – This category is addressing the environment in the building and how it is affecting the tenants or employees inside. In this category, the project receives points for indoor air quality, temperature, lighting, usage of daylight, ventilation, and indoor pollution.
Adding air filters and systems for moisture control in the building will be awarded by the LEED program with a certain number of points. These filters and systems will help in reducing allergens and molds. Then making sure that the HVAC vents are not connecting between garages, as well as installing exhaust vents in the kitchen.
Education and Awareness – This category might seem that is not connected with protecting the environment. Actually, by educating the occupants of the LEED standards, they will be able to keep their homes, or buildings energy efficient in the years to come. LEED is awarding points for educating your tenants on how to, for example, use system for recycling rainwater, how to limit the use of water, etc.
According to USGBC, “A property is only as an environmentally friendly as the way it is used” For example, if a homeowner has the heater on for the whole winter, but keeps his windows open all the time, no matter if his appliances are marked with Energy Star, they aren’t saving energy.
How to become LEED certified?
The process of becoming LEED certified has 4 main steps:
1. Register on the site, submit your project, and pay the registration fee;
2. Apply for the certification by submitting the completed application and paying the fee for certification review;
3. Review your LEED application by the Green Building Certification Institute;
4. Certify – Receiving the institute’s decision for certification.
The first step in the certification process is to register at http://www.usgbc.org/leed and then pay the fee for registration, between $1200 for USGBC members and $1500 for non-members. Then you need to appoint all of your team members including project administrator and agent.
and then pay the fee for registration, between $1200 for USGBC members and $1500 for non-members. Then you need to appoint all of your team members including project administrator and agent.
The owner has the overall control of the process and has priority in receiving responses from the LEED reviewers. Whereas the project administrator is responsible for overseeing the project, delegating and supervising the rest of the team members, and checking the accuracy of the application.
The second step is preparing the application process by identifying the LEED credits that need to be pursued and assigned to the team members. The team is responsible for gathering the needed information, performing analysis and calculations, and preparing the documentation that demonstrates the achievement of the prerequisites.
The project administrator needs to do a quality check of the completed documents and cross-check prerequisites and credits, to be sure that the data in the application is accurate.
The third step is reviewing the application by the Green Building Certification Institute after you have submitted it and paid the fee for certification. In this step, you still need to be an active participant.
-
Preliminary Review – GBCI is checking the application for compliance with the rating system of choice and credits, and for completeness. GBCI will give the preliminary review report within 20-25 business days.
-
Final Review – This stage is allowing you to submit additional information requested by GBCI. Then they will revise the newly submitted credits and prerequisites and respond with the final review report within 20-25 business days.
The review can be for all rating systems or split review (BD+C and ID+C).
The fourth step is receiving the Institute’s review results for certification. You can accept the decision or appeal it.

Twelve benefits of being LEED Certified?
In order to become LEED Certified, you must take some steps in achieving bigger energy efficiency, decreasing the carbon footprint of your building, and using your resources wisely. All of this is showing your commitment to having an environmental sustainability to your customers and community.
Even though acquiring LEED certification is an expensive process, in the long run having a high LEED score will help you in saving a significant amount of money. Especially for buildings that are for commercial use, the overhead will reduce exponentially. Maximizing the use of natural light, reducing water consumption, and improving energy efficiency will help in reducing the utility bills and operational costs.
Having a great indoor environment will help you to have a productive and healthier workplace for all the users of the building. Additional benefits of receiving a LEED Certification are:
1. Increased value of the building;
2. Reducing costs for operation and maintenance of the building;
3. Reduced use of water and energy;
4. Promoting better relationships between employees;
5. Promoting a better indoor environment and air quality;
6. Attracting companies that also have goals for a green, sustainable environment to be tenants in your building;
7. Increased employee satisfaction, productivity, and retention;
8. Reducing the number of sick days;
9. Reduced liability;
10. In order to optimize the performance of the building incorporating additional innovation processes;
11. During the construction process, reducing the construction waste;
12. Promoting the use of recycled resources and materials.

LEED certification system is widely recognized for environmentally sustainable buildings and homes and is accepted by engineers, architects, developers, and other professionals in the building industry. However, every business is different, and you need to do some research and assessments to check if the LEED certification is for you.
Related Questions
What is Energy Star? Energy Star is a program from the Department of Energy and Environmental Protection Agency that is promoting energy efficiency by providing certification to consumer products and buildings that meet strict criteria. The label of Energy Star can be found in new homes, industrial buildings, commercial; buildings, and more than 75 categories of products.
For example, one home to be Energy Star certified needs to be more than 20% energy efficient than the regular homes. This can be achieved by making a combination of a few factors, such as installing Energy Star certified light bulbs and appliances, thermal enclosure system, ventilation, high-efficient cooling, and heating system, water management system, and more.
LEED Certification vs. LEED Accreditation
When talking about LEED, there are two terms that are commonly confused.
LEED Certification is referring to brand new buildings- their design, construction, and maintenance while using the best practices for having a green, sustainable building that is energy efficient, as well as buildings that undergo major renovations honoring the same practices.
LEED Accreditation is referring to people who have knowledge regarding green building principles by passing the exam for receiving professional credentials.
What are the benefits of being LEED Accredited? Having a LEED Accreditation will provide you with a valuable overview of what sustainable development and green building mean. There are seven personal and employer benefits:
-
Accreditation makes you a valuable asset to your employer, potential client or employer;
-
Even if you have no prior experience, you have the option for a new career path;
-
Expanding your professional reach by being listed on the website directory of USGBC’s LEED professionals;
-
Being qualified for projects that require the participation of a LEED accredited professional;
-
Get recognition for being involved in LEED certification processes;
-
Qualify for promotions and salary increases;
-
Encouraging and promoting a higher understanding of the LEED processes around the world.
Join Open Sourced Workplace



